What Is an Aortic Aneurysm?
An aortic aneurysm is a weakened, ballooned section of the aorta—the body’s largest artery, responsible for carrying blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Over time, this bulge can grow and may eventually rupture, leading to a life-threatening emergency. Unfortunately, most aneurysms cause no symptoms until they become large or begin to leak.
At Vascular Clinic, we emphasize early detection, ongoing surveillance, and timely treatment to prevent rupture and preserve life.
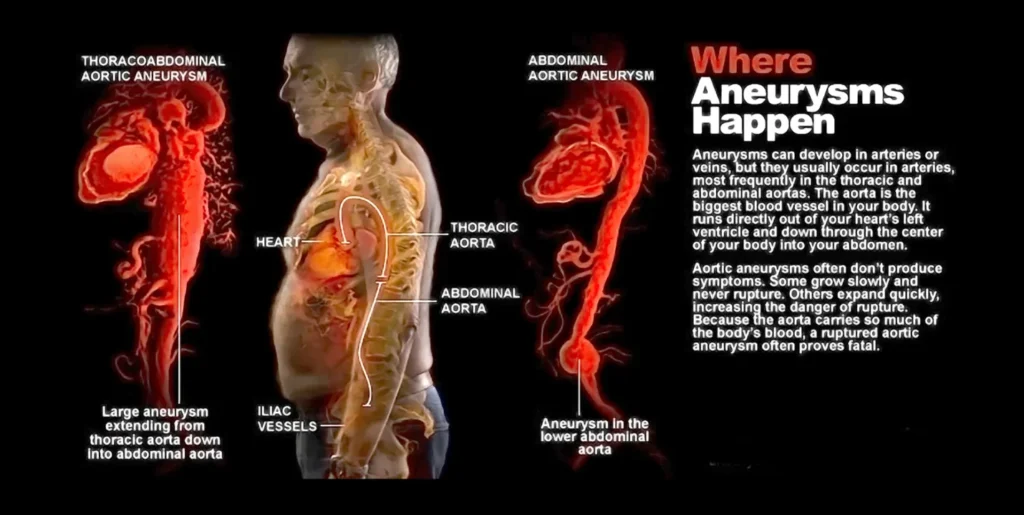
Types of Aortic Aneurysms
There are two main types of aortic aneurysms:
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA): Occurs in the section of the aorta that runs through the abdomen
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm (TAA): Occurs in the section of the aorta that passes through the chest
Both types require careful monitoring and a personalized treatment plan to prevent complications.
How We Monitor Aneurysms
At Vascular Clinic, we use a structured surveillance program designed to detect aneurysms early and track their growth over time. We use:
- Noninvasive imaging such as ultrasound or CT scans
- Serial clinic visits with ongoing risk assessment
- Measurement tracking to determine when treatment is indicated
When an aneurysm reaches a certain size or shows signs of rapid growth, we recommend intervention to prevent rupture.
Treatment Options
Whenever possible, we use minimally invasive techniques to treat aortic aneurysms. However, we are equally equipped to perform open surgical repair when necessary.
- Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR/TEVAR)
- Open Surgical Repair
Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR/TEVAR)
For suitable aneurysms, we perform EVAR (for abdominal aneurysms) or TEVAR (for thoracic aneurysms). This involves:
- Small incisions in the groin
- Insertion of a stent graft using catheter-based techniques
- Precise placement of the graft inside the aorta to seal off the aneurysm
EVAR/TEVAR is our first-line approach when the patient’s anatomy is favorable.
Advantages:
- No large incisions
- Shorter hospital stay (typically 1–2 days)
- Faster recovery
- Reduced complication risk
Open Surgical Repair
When aneurysm anatomy is complex or unsuitable for endovascular repair, open surgery may be required. This involves:
- A larger incision in the abdomen or chest
- Surgical removal of the aneurysmal segment
- Graft replacement of the affected portion of the aorta
Open repair is time-tested and remains the safest option in certain cases. While recovery is longer, the durability of repair is excellent.
Abdominal and Thoracic Video

Individualized Aneurysm Care
Every aneurysm is different. Our team evaluates:
- The size, location, and shape of your aneurysm
- Your medical condition and surgical risk profile
- Imaging findings and anatomical suitability for EVAR/TEVAR
Based on this, we recommend the safest and most effective treatment—whether minimally invasive or open.
What to Expect
Before Treatment:
- Imaging studies (ultrasound or CT angiography)
- Comprehensive evaluation during clinic visits
- Discussion of risks, benefits, and treatment options
During the Procedure:
- EVAR/TEVAR: small incisions, stent placement, no large cuts
- Open repair: traditional surgery for select patients with complex aneurysms
- All procedures are performed in a hospital setting with expert vascular surgical care
After the Procedure:
- Most EVAR/TEVAR patients go home within 1–2 days
- Open surgery patients typically stay longer but are closely supported
- Continued imaging follow-up and clinic visits to ensure long-term success
Frequently Asked Questions
How are aortic aneurysms diagnosed?
Through imaging such as abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, or CT angiography. These detect the size and location of the aneurysm.
When does an aneurysm need to be treated?
Intervention is generally recommended when the aneurysm exceeds 5.0–5.5 cm in diameter, grows rapidly, or shows signs of leaking.
Is endovascular repair always possible?
No. It depends on the aneurysm’s anatomy. If EVAR or TEVAR is not safe, we perform open surgery with the same goal: preventing rupture.
What is the recovery like?
EVAR/TEVAR typically involves a short hospital stay and rapid recovery. Open surgery requires more time but offers excellent long-term durability.
Why Choose Vascular Clinic?
- Board-Certified Vascular Surgeons
- Advanced Endovascular and Open Surgical Expertise
- Minimally Invasive First Approach
- Comprehensive Imaging and Surveillance
- Customized Care Plans Based on Anatomy and Risk
Our goal is simple: prevent rupture, protect your future, and guide you through every step with clarity and compassion.




